- Cooling Load Calculation Rts Programming
- Cooling Load Calculation Rts Programs
- Cooling Load Calculation Rts Program 2
- See Full List On Carrier.com

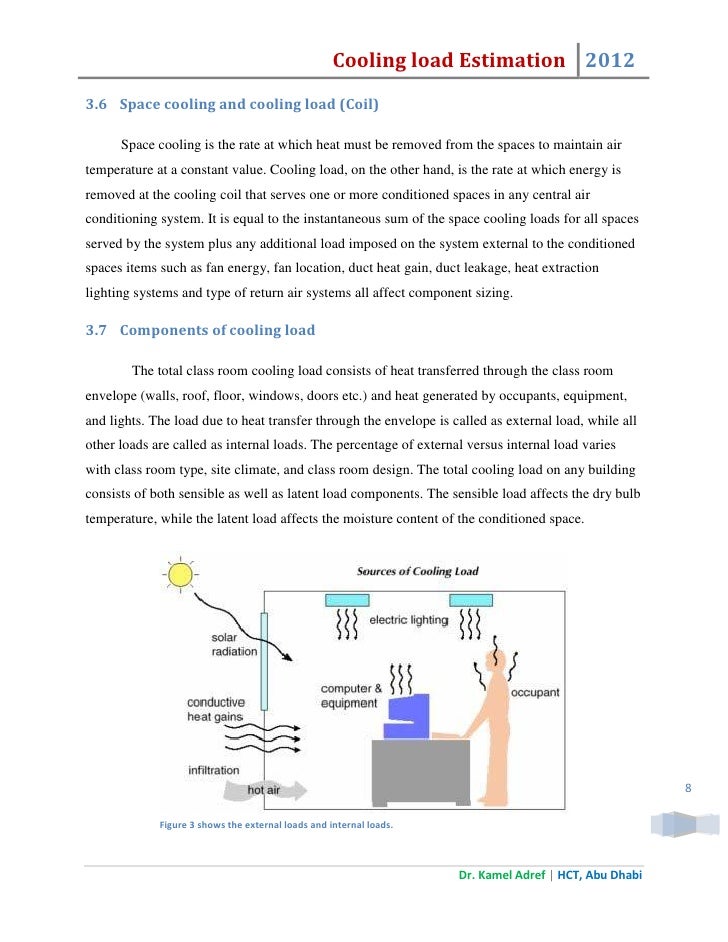
[Note: this version uses I-P units only]The 2017 Radiant Time Series (RTS) Method Load Calculation Spreadsheets (in I-P units) are intended as an educational tool both for the student and for the experienced engineer wishing to explore the RTS method. They have been updated for use in the examples found in Chapter 18, Nonresidential Cooling and Heating Load Calculations, of the 2017 ASHRAE Handbook--Fundamentals.These spreadsheets allow the user to perform RTS cooling load calculations for lights, people, equipment, walls/roofs, and fenestration components. Calculate component loads for design day weather profiles for any month. Updated weather data for stations in the United States, Canada, and elsewhere around the world from the 2017 Fundamentals volume are included for ease of user selection. Solar equations in the spreadsheets are applicable to the southern hemisphere, as well.Calculate cooling and heating loads for individual rooms or block load zones. Use the 12-month cooling calculations to determine the month and time of peak cooling load for each room or block load zone. Room/zone worksheets can be copied and modified within the spreadsheet to analyze as many rooms or zones as desired; the number of rooms/zones is limited only by the available computer memory.System Requirements: WinZip and Microsoft Excel. File size is 25 MB, so we recommend a broadband internet connection when attempting to download. Zip file includes 2 files totaling 99 MB.
Citation: ASHRAE Radiant Time Series (RTS) Method Load Calculation Spreadsheets, 2017
Cooling Load Calculation Rts Programming
Join channel by clicking link given below to get access to particular material used in the videohttps://www.youtube.com/channel/UC4Wvckp5qJ2MoY5fyGJTFQ/join. HVAC COOLING LOAD CALCULATIONS AND PRINCIPLES 1.0 OBJECTIVE Cooling load calculations may be used to accomplish one or more of the following objectives: a) Provide information for equipment selection, system sizing and system design. B) Provide data for evaluating the optimum possibilities for load reduction.
Cooling Load Calculation Rts Programs
The general procedure for calculating cooling load for each load component (lights, people, walls, roofs, windows, appliances, etc.) with RTS (ASHRAE) is as follows:
- Calculate 24 h profile of component heat gains for design day (for conduction, first account for conduction time delay by applying conduction time series).
- Split heat gains into radiant and convective parts.
- Apply appropriate radiant time series to radiant part of heat gains to account for time delay in conversion to cooling load.
- Sum convective part of heat gain and delayed radiant part of heat gain to determine cooling load for each hour for each cooling load component.
Cooling Load Calculation Rts Program 2
After calculating cooling loads for each component for each hour, the engine sums those to determine the total cooling load for each hour and selects the hour with the peak load for design of the air-conditioning system. The engine repeats this process for multiple design months to determine the month when the peak load occurs.
See Full List On Carrier.com
Heat gain through exterior opaque surfaces is derived from the same elements of solar radiation and thermal gradient as that for fenestration areas. It differs primarily as a function of the mass and nature of the wall or roof construction, because those elements affect the rate of conductive heat.